1
? What are viruses associated with respiratory infections
“Viruses associated with respiratory infections” refer to the viruses that invade and proliferate in the epithelial cells of the respiratory tracts that could cause respiratory and systemic symptoms
2
? What are the common viruses associated with respiratory infections
Viruses from the family Orthomyxoviridae (influenza viruses), the family Paramyxoviridae (paramyxoviruses, respiratory syncytial virus, measles virus, mumps virus, Hendra virus, Nipah virus and human metapneumovirus), the family Togaviridae (Rubella virus), the family Picornaviridae (rhinovirus), and the family Coronaviridae (SARS coronavirus) are the common respiratory viruses. In addition, adenovirus, reovirus, coxsackie virus, ECHO virus, herpes virus, etc. can also cause infectious respiratory diseases
3
? What are coronaviruses
Coronavirus are unsegmented single-stranded positive-strand RNA viruses. They belong to the order Nidovirales, the family Coronaviridae, and the subfamily Orthocoronavirinae, which is divided into α, β, γ, and δ genera according to their serotypic and genomic characteristics. Coronaviruses belong to the genus Coronavirus of the family Coronaviridae. It is named after the wreath-shaped protrusions on the envelope of the virus
4
? What are the shape and structure of coronaviruses
Coronaviruses have an envelope encasing the RNA genome), and the virions (the whole viruses) are round or oval, often polymorphic, with a diameter of 50 to 200 nm. The novel coronavirus is 60 to 140 nm in diameter. The spike protein is located on the surface of the virus and forms a rod-like structure. As one of the main antigenic proteins of the virus, the spike protein is the main structure used for typing. The nucleocapsid protein encapsulates the viral genome and can be used as a diagnostic antigen
5
? How are coronaviruses classified
Most coronaviruses infect animals. Currently, three types of coronaviruses have been isolated from humans: Human Coronaviruses 229E, OC43, and SARS coronavirus (SARS-CoV). There are 6 types of coronaviruses previously known to infect humans. 229E and NL63 (of alphacoronaviruses), OC43 (of betacoronaviruses), HKU1, Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV), and Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (SARS-CoV). Recently, a novel coronavirus was isolated from the lower respiratory tract of patients in Wuhan, who were suffering from pneumonia due to unknown causes (The World Health Organization (WHO) called it 2019- nCoV while the International Committee on the Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) named it SARS-CoV-2. It was subsequently confirmed that the virus is capable of human-to-human transmission. This novel coronavirus is very similar in terms of the genome sequences to six previously discovered coronaviruses. An analysis of their genetic sequence homology revealed that the new virus has many similarities with SARS-CoV. This novel coronavirus is now classified as a beta-coronavirus
6
? Which wild animals carry coronaviruses
Many wild animals carry pathogens and are potential transmission vectors of certain contagious diseases. Bats, civets, badgers, bamboo rats, and wild camels, etc. are known hosts of coronaviruses. The outbreak of novel coronavirus pneumonia originated in Wuhan has many similarities to the SARS outbreak in Guangdong back in 2003: both began in the winter; the initial cases were traced to contacts with fresh, live animals in a market; both were caused by a previously unknown coronavirus
Due to the similarity of the genomic sequences between the novel coronavirus and a coronavirus found in bats, which is 85% or higher, it is speculated that bats are the natural hosts of the novel coronavirus. Like the SARS coronavirus that caused the outbreak in 2003, the novel coronavirus is likely to have intermediate hosts between bats and humans yet unknown to us. Therefore, one should refrain from consumption of uninspected wild animals or uncooked food such as meat sold by roadside sellers
7
? How do coronaviruses transmit from animals to humans
Many coronaviruses that infect humans could be found in bats, which are natural reservoirs of coronaviruses. Bats are likely to be the original host of the novel coronavirus. Transmission from bats to humans might have occurred after mutation via an intermediate host(s). The genomic sequence analysis showed a more than 85% homology between the novel coronavirus and a coronavirus in bats. However, there are several other possible intermediate hosts between bats and humans, which have not been confirmed yet. Animal-to-human or human-to-human transmission relies mainly on two routes: contacts and droplets
The coronaviruses that are currently known to cause pneumonia in humans include HKU1, SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, and 2019-nCoV
8
? How resilient are coronaviruses in different environment
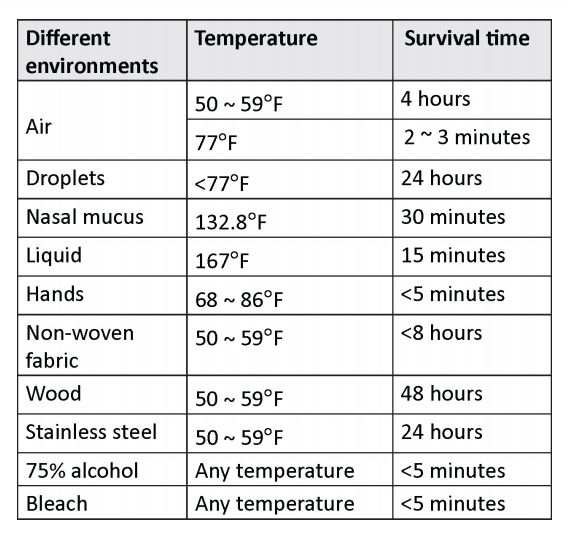
Viruses generally can survive for several hours on smooth surfaces. If the temperature and humidity permit, they can survive for several days. The novel coronavirus is sensitive to ultraviolet rays and heat. Sustained heat at 132.8ºF for 30 minutes, ether, 75% alcohol, chlorine-containing disinfectants, peracetic acid, chloroform, and other lipid solvents can effectively inactivate the virus. Chlorhexidine (also known as chlorhexidine gluconate) also effectively inactivates the virus
The survival time of the novel coronavirus 2019-nCoV at different environmental temperatures is as follows
9
? How virulent is the 2019-nCoV
Common coronaviruses mainly infect adults or older children, causing the common cold. Some strains can cause diarrhea in adults. These viruses are mainly transmitted by droplets, and can also be spread via the fecal-oral route. The incidence of corona virus infection is prevalent in winter and spring. The incubation period for coronaviruses is usually 3 to 7 days
2019-nCoV is a coronavirus that underwent antigenic mutations. The incubation period of the virus is as short as 1 day but generally considered to be no longer than 14 days. But it should be noted that some reported cases had an incubation period of up to 24 days
To measure the degree of harm caused by a virus, both infectivity and lethality should be considered. The new coronavirus is highly-infectious and can be fatal, but its lethality has not been determined at present
10
? Can humans develop immunity to 2019-nCoV
Scientific data on the level and the duration of protective immune antibodies produced in patients after infection of the novel coronavirus remain scarce. In general, the protective antibodies (immunoglobulin G, IgG) against a virus can be produced two weeks or so after an infection, and may exist for several weeks to many years, preventing re-infection of the same virus after recovery. Currently efforts are underway to test whether recently recovered from 2019-nCoV infection carry protective antibodies in the blood
11
? (What is Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS
Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) is a disease caused by SARS-CoV. The main symptoms of SARS include fever, cough, headache, muscle pain, and other symptoms of respiratory infection. Most SARS patients recover with or without medical treatment. Its fatality rate is about 10%; those over 40 years of age or with underlying diseases (such as coronary heart disease, diabetes, asthma, and chronic lung diseases) are most at risk to develop the fatal disease
12
? (What is Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS
Middle East Respiratory Syndrome is caused by MERS-CoV. It was first reported in middle-eastern countries including Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates etc. People who are infected by MERS-CoV can develop acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), while the most common manifestations being fever with tremors, coughing, shortness of breath, sore muscles and gastrointestinal symptoms such as diarrhea, nausea, vomiting or stomachache. Severe cases are featured by respiratory failure which require mechanical ventilation and supportive treatment in ICU. Some patients developed organ failures, especially renal failure and sceptic shock which eventually led to death. The case fatality rate is about 40%. Since the onset of the first MERS case in September 2012 until May 2015, MERS cases have been reported in 25 countries around the world, posing a serious threat to public health
13
? What is novel coronavirus ? Why has it become epidemic
The newly discovered coronavirus is a mutated novel coronavirus (β genus), which is named 2019-nCoV by the WHO and SARS-CoV-2 by the ICTV. On January 10, 2020, genomic sequencing of the first sample of 2019-nCoV was completed, and the viral genomic sequences of five more samples were subsequently announced. Due to the antigenic mutations that made this corona virus new to humans, the general population lacks immunity against the new strain. Furthermore, there are more than one routes of transmission for this virus. These factors resulted in the novel coronavirus becoming epidemic





 رد مع اقتباس
رد مع اقتباس